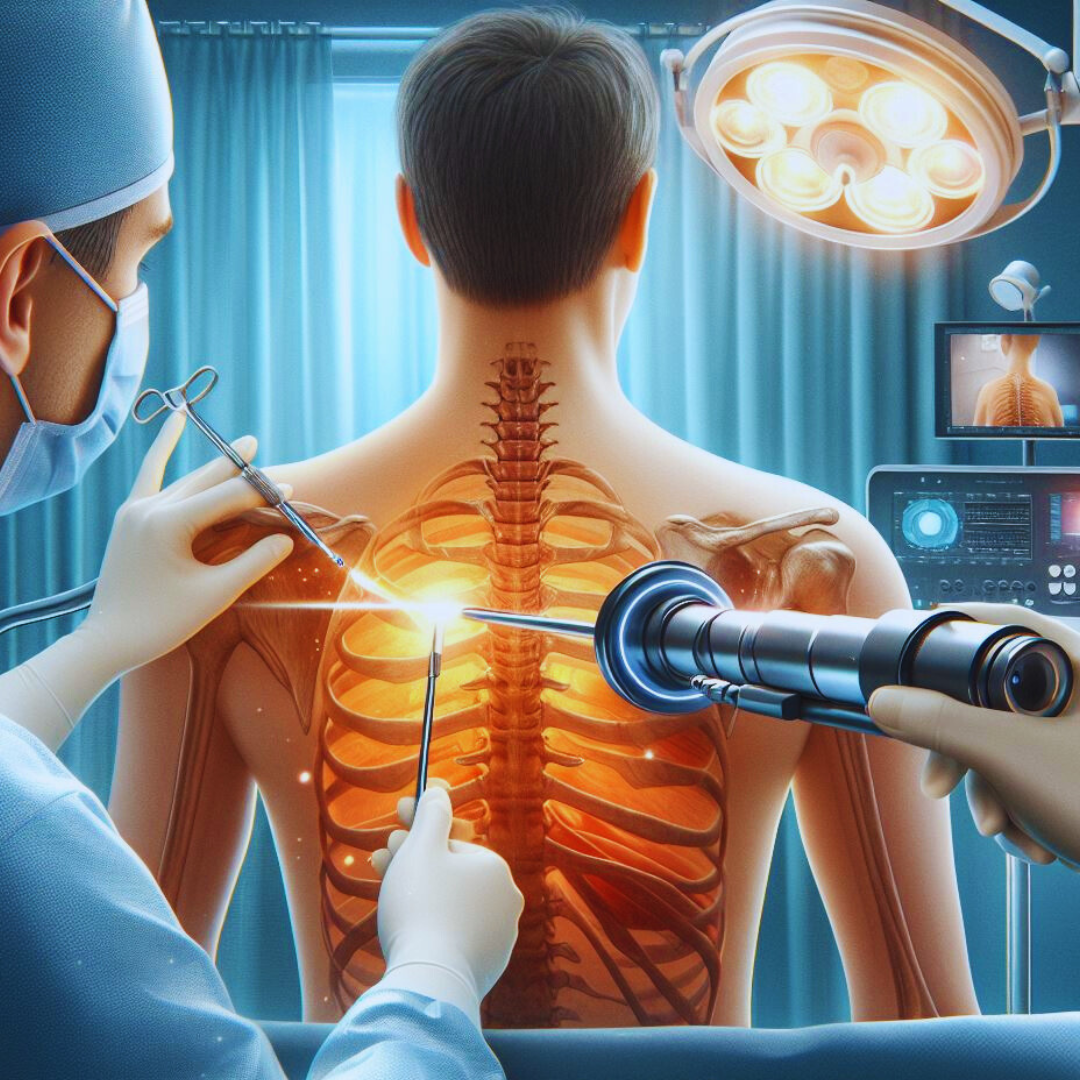
Thoracoscopy
- Proficient in performing thoracoscopy procedures to visualize and intervene within the pleural cavity, aiding in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of pleural disorders.

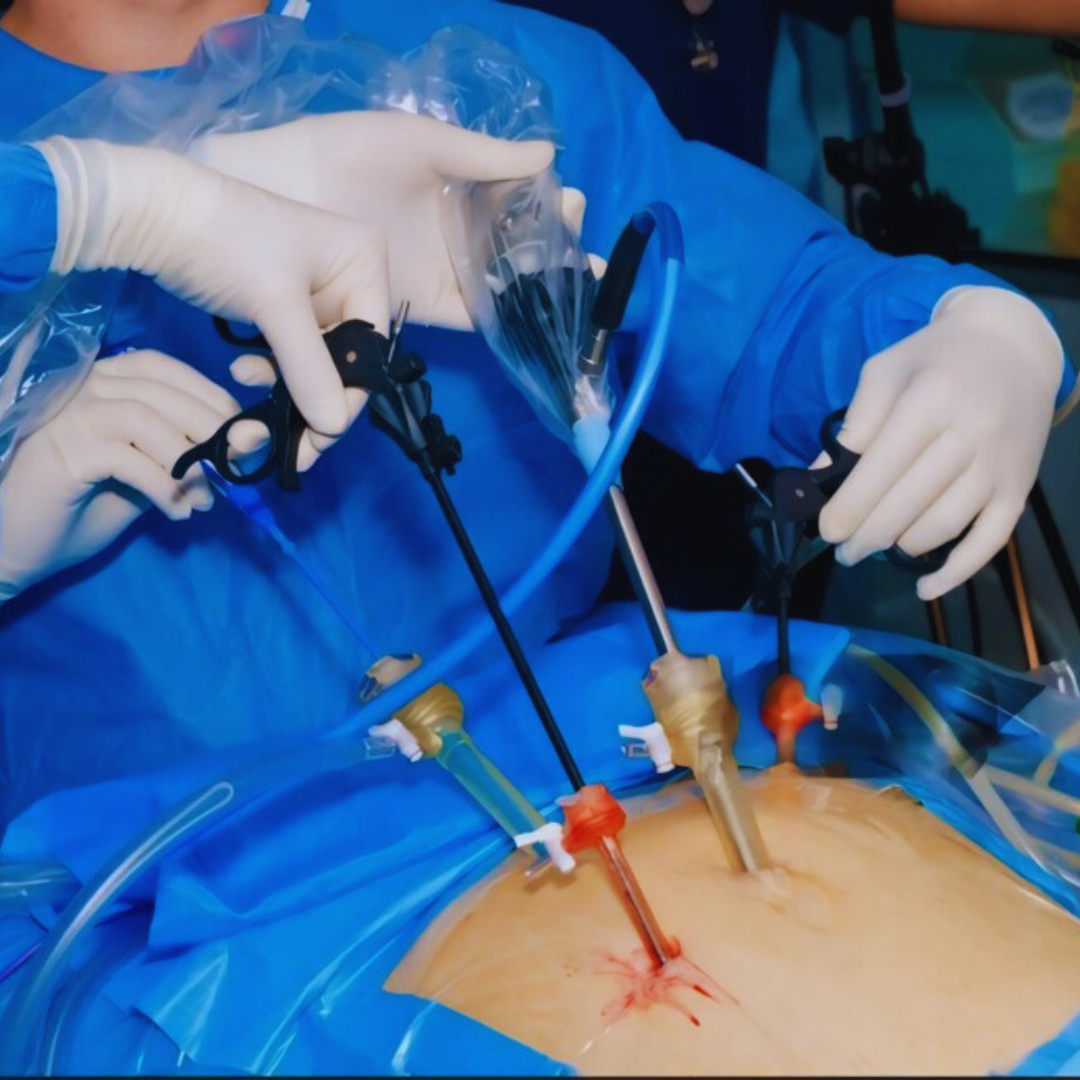
How does it work?
During a thoracoscopy, the patient is placed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and immobility throughout the procedure. Small incisions (ports) are made in the chest wall, through which the thoracoscope and other surgical instruments are inserted. The thoracoscope provides real-time video images of the pleural cavity, allowing the surgeon to visualize and manipulate tissues as needed. Once the necessary diagnostic or therapeutic interventions are completed, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips. Thoracoscopy typically results in less pain, shorter recovery times, and reduced risk of complications compared to traditional open surgery.