
Inter Coastal Drainage
- Proficient in performing Intercoastal Drainage procedures to alleviate pleural effusions, pneumothorax, and other thoracic conditions, promoting respiratory function and patient comfort effectively.

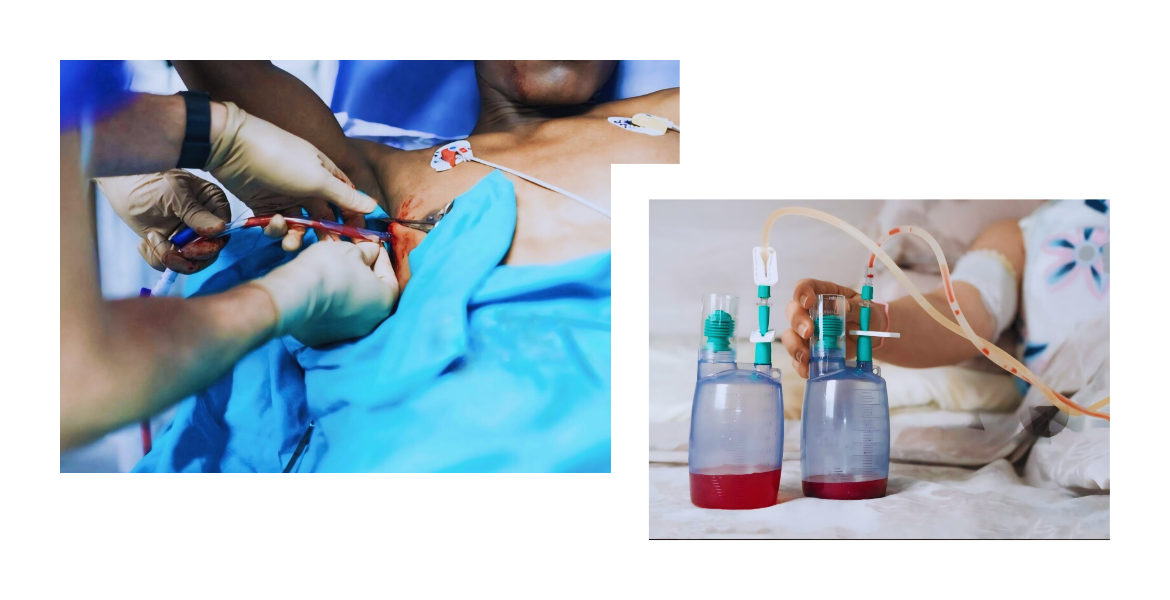
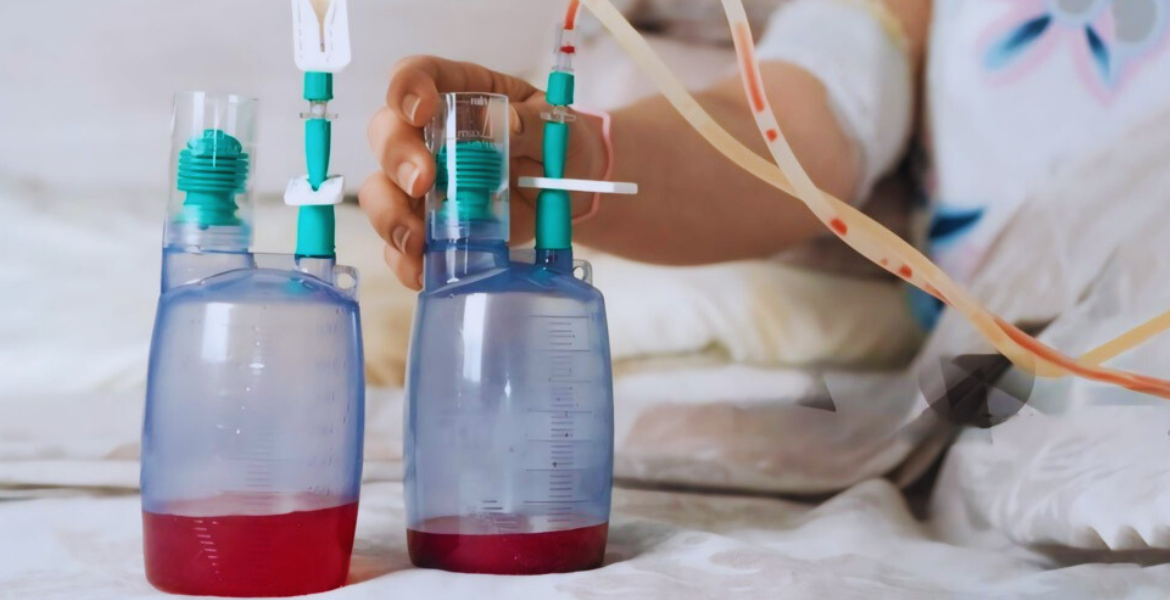
How does it work?
During intercoastal drainage, a small incision is made in the chest wall, and a chest tube or catheter is inserted into the pleural cavity under sterile conditions. The tube is connected to a drainage system, which allows fluid or air to be removed from the pleural space. The drainage system may consist of a collection chamber, a water seal, and suction control to regulate the flow of fluid or air. The tube remains in place until the underlying condition resolves, and the fluid or air accumulation is adequately drained. Regular monitoring and assessment of drainage output and patient status are essential to ensure optimal outcomes.

